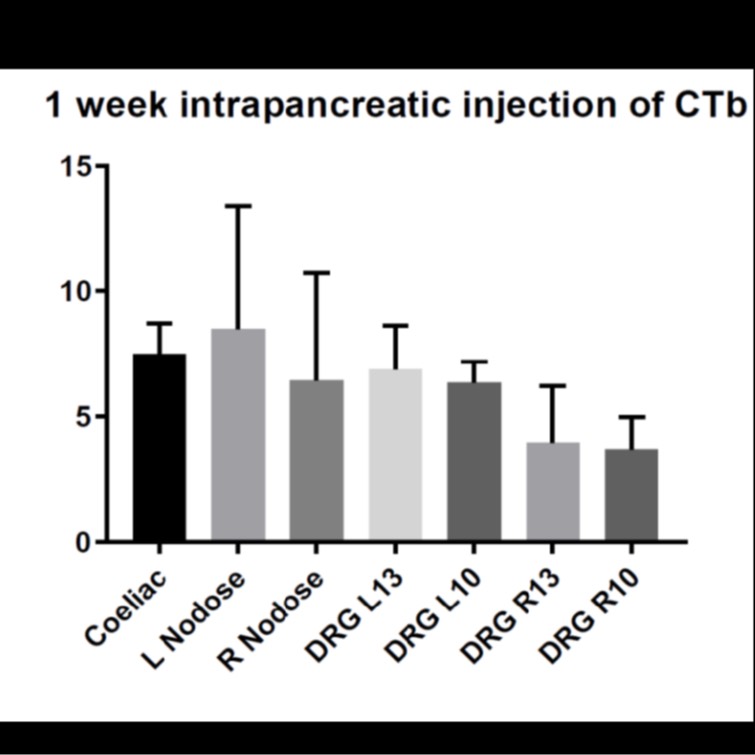
Quantification of Cholera Toxin Subunit Beta (CTb) positive neurons in the coeliac nodose and dorsal root ganglia 1 week after pancreas injection in mice
Quantification of CTB in coeliac, nodose, and dorsal root ganglia 1 week after intrapancreatic injection
Dataset Overview
Study Purpose: This study was undertaken to define the neural connectivity of the pancreas.
Data Collection: The neuronal tracer Cholera Toxin Subunit Beta (CTb) conjugated with a fluorophore (AlexaFluor 488) is injected into the parenchyma of the pancreas. 1 week later, neuronal ganglia, including Nodose, Coeliac and thoracic Dorsal Root Ganglia are harvested. Tissue clearing and staining for CTb is performed using the iDisco protocol. Image acquisition is done utilizing a confocal microscope. Further, the quantification of CTb-positive neurons is assessed using IMARIS software.
Primary Conclusion: None stated.
Curator's Notes
Experimental Design: Samples (n=31) were obtained from 6 mice whose pancreas was injected with CTb to mark neurons. Tissue from the Nodose, Coeliac and thoracic Dorsal Root Ganglia were harvested for histology.
Completeness: this dataset is a part of a rager study: Quantification of CTB in coeliac, nodose, and dorsal root ganglia.
Subjects/Samples: Samples were taken from 6 male, 3-month-old adult, C57BL/6J mice weighing 24-27 g.
Primary vs. Derived: Experimental documents are available as images for each peripheral ganglia in the primary folder. A summary of the histology results is available in the derived folder.
Important Notes: The documents folder and protocols are highly informative.
Files
0 - 0 of 0 files
About this dataset
Publishing history
Cite this dataset
Tags
References
Is Supplemented by
Jimenez Gonzalez, M., Stanley, S., & Li, R. (2020). iDISCO Clearing and Staining of Pancreas v1. https://doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.baxbifin
