Mid-lumbar (L3) epidural stimulation effects on bladder and external urethral sphincter in non-injured and chronically transected urethane-anesthetized rats
In the current pre-clinical study, the L3 was targeted with scES to examine whether the EUS could be modulated under intact and chronic complete SCI conditions.
Dataset Overview
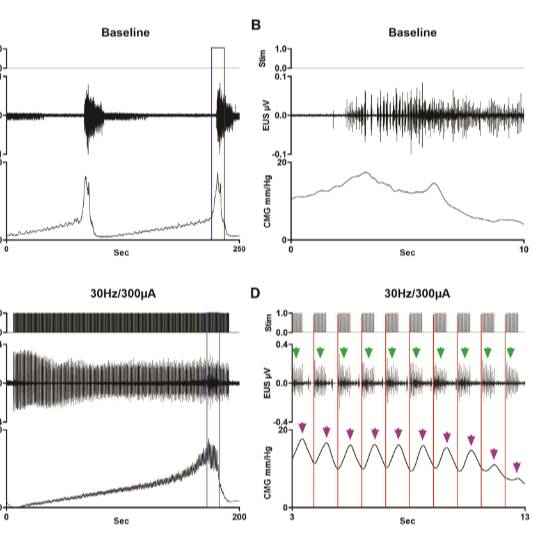
Study Purpose: This study was conducted to target L3 with spinal cord epidural stimulation (scES) to examine whether the external urethral sphincter (EUS) could be modulated under intact and chronic complete spinal cord injury (SCI) conditions.
Data Collection: Using electromyography of the EUS and cystometrogram, we measured the motor outcomes of the lower urinary tract in response to L3 scES.
Primary Conclusion: The results of this study demonstrate that scES at the L3 spinal level can modulate the activity of both the bladder and EUS in intact and SCI rats.
Curator's Notes
Experimental Design: Spinal cord epidural stimulation (scES) mapping at L3 was performed to identify parameters for bladder and bowel storage and/or emptying. Using spinally intact and chronic transected female rats in acute urethane-anesthetized terminal preparations, scES was systematically applied using a modified Specify 5-6-5 (Medtronic) electrode during bladder filling/emptying cycles while recording bladder and colonic/rectal pressures and external urethral and anal sphincter EMG activity
Completeness: This dataset is complete.
Subjects & Samples: A total of 18 female Wistar rats (RRID:RGD_38548927) were used for this study. Half the animals (n = 9) received a complete spinal cord transection at the T9 spinal level, whereas a second group (n = 9 surgical shams) had a laminectomy but no SCI.
Primary vs derivative data: Electrophysiology recordings are done using Spike2 software, which contains the setup for all of the channels being recorded (EUS, EAS, bulbo, 2 cm probe, 10 cm probe, leaks, stim marker, keyboard input). The primary data folder is organized by the subject IDs. There is no derivative data folder.
Files
0 - 0 of 0 files
About this dataset
Publishing history
Cite this dataset
Tags
References
Described by
Medina-Aguiñaga, D., Hoey, R. F., Wilkins, N. L., Ugiliweneza, B., Fell, J., Harkema, S. J., & Hubscher, C. H. (2023). Mid-lumbar (L3) epidural stimulation effects on bladder and external urethral sphincter in non-injured and chronically transected urethane-anesthetized rats. Scientific Reports, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-39388-9
