A 3D human whole-body model with integrated organs vasculature musculoskeletal and nervous systems for mapping nerves
The generated body scaffold was fitted to data, and the organ fiducial markers were embedded in the human whole-body. The landmarks were obtained from image data and also were defined in the body scaffold. Furthermore, nerve centrelines are added.
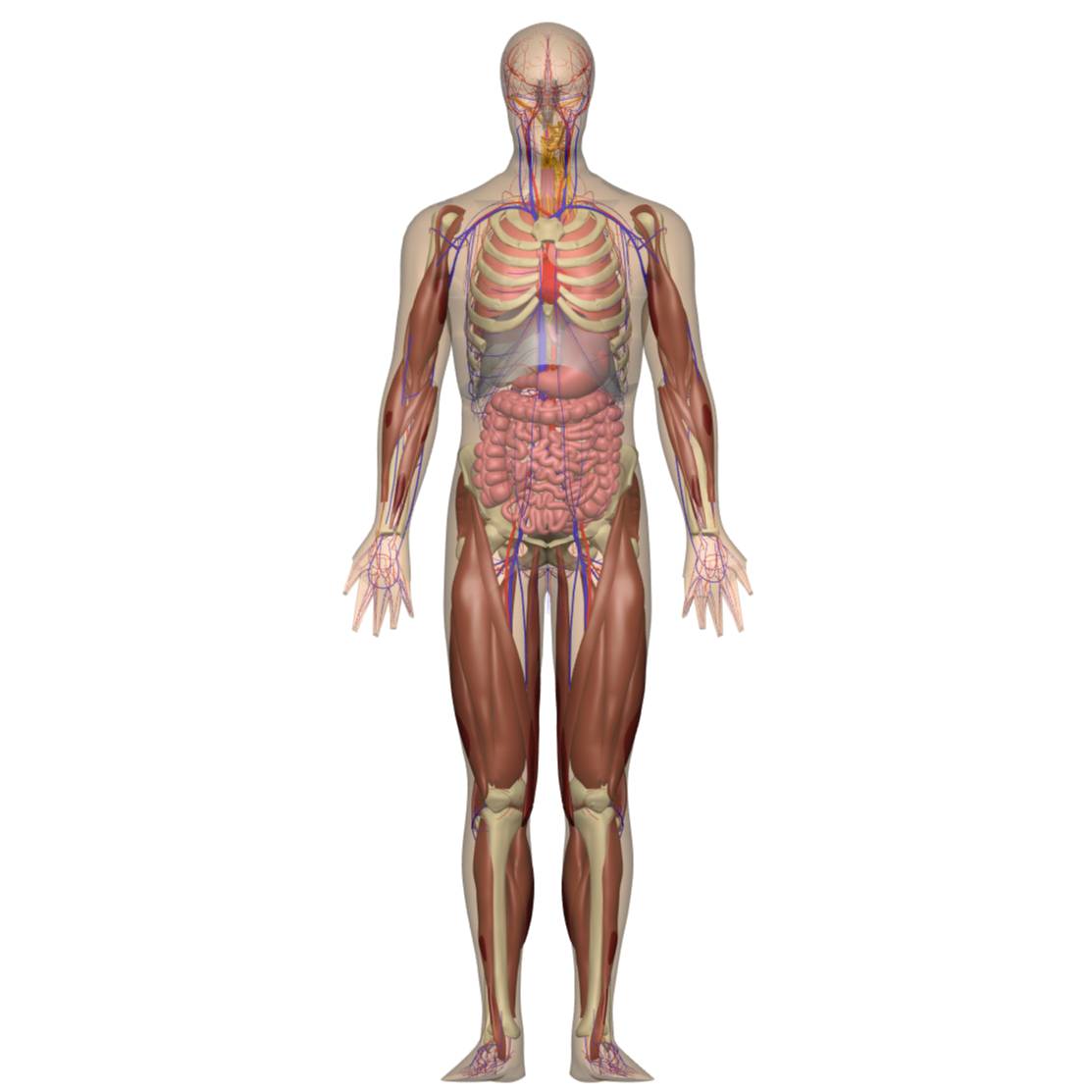
Dataset Overview
Study Purpose: The goal of this work is to create an annotated human whole-body scaffold with embedded organs, musculoskeletal, vasculature, and nervous systems.
Data Collection: The generic scaffold is created based on the generic body coordinates that fit data for the human whole-body. The generated organ scaffolds were embedded by embedding the fiducial markers. The fiducials for the nerves are placed by best guess into the human body using literature to check and verify the location. The muscles and bones are fitted to data. Additionally, the data for the vasculature system was obtained from Anatomography. An automated workflow was developed to obtain the central path of the vessels. The algorithm calculates the radius for each vessel, and then cubic Hermite splines are fitted to the central paths using least-square minimization to achieve smooth and continuous curves.
Primary Conclusion: None stated
Curator’s Notes
Experimental Design: Not applicable.
Completeness: The study is ongoing and potentially will link to other datasets where the data is used for mapping onto the scaffold.
Subjects & Samples: The body scaffold is not subject/sample-specific, but the morphed scaffold was fitted to the given data.
Primary vs derivative data: The primary folder contains the mapping tool provenance data file describing the software environment used to create this dataset. The primary folder also contains the settings files, which in conjunction with the software information in the provenance file will reproduce the output files stored in the derivative folder. The derivative folder contains JSON files that are used to generate a webGL visualization of the scaffold on the SPARC portal.
Code Availability: Scaffold Mapping Tools
Files
1 - 0 of 0 files
