Evaluation of bilateral gastric electrical stimulation to improve energy balance regulation in female Sprague-Dawley rats consuming a 45% high-fat diet
Microstructural analysis of food intake as a behavioral endpoint to determine the effect of bilateral electrical stimulation of the forestomach on the consumption of a 45% high fat diet by female Sprague-Dawley rats.
Dataset Overview
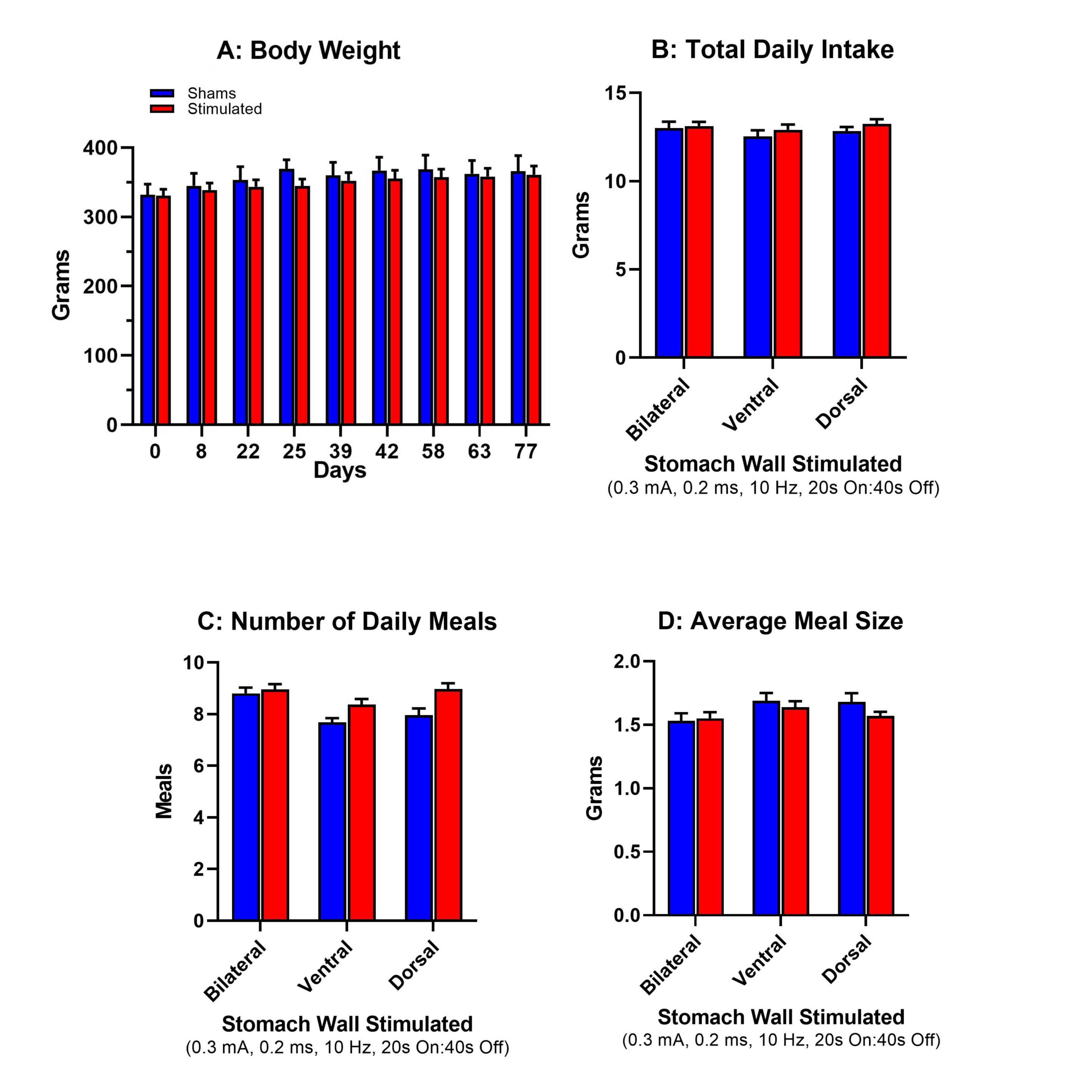
Study Purpose: To the best of our knowledge, electrical stimulation of the stomach has been limited to the ventral wall of the organ and found to be relatively ineffective at improving energy balance regulation in adult female Sprague-Dawley rats. Unilateral stimulation of the ventral stomach wall ignores the fact that the vagus nerve innervates both the ventral and the dorsal walls of the stomach. Thus, taking into account the bilateral innervation of the forestomach by the vagus nerve, we implanted two patch electrodes, one at each site on the ventral and the dorsal walls of the stomach of female rats that is known to contain the highest density of overlapping vagal terminals located in the circular and longitudinal muscle (i.e., intramuscular arrays). Consumption of a 45% high-fat maintenance diet while the stomach was stimulated both bilaterally and unilaterally was recorded to determine if there was an improvement in energy balance regulation to this high-fat diet challenge.
Data Collection: Microstructural analysis of food intake as a behavioral endpoint to determine the effect of bilateral electrical stimulation of the forestomach on the consumption of a 45% high fat diet by female Sprague-Dawley rats.
Primary Conclusion: The body weight and food intake of the unstimulated female shams did not differ from those of the stimulated female rats under the conditions tested (i.e., bilateral and unilateral stimulation of the stomach walls). The stimulated and unstimulated sham groups had similar blood glucose levels at the completion of the study.
Curator's Notes
Experimental Design: Eight female Sprague-Dawley rats, each with two patch electrodes implanted on the serosal wall of the forestomach (one on the ventral wall of the forestomach and a second on the dorsal wall of the forestomach), were stimulated continuously for 14 days under three different conditions (bilateral stimulation of both walls of the forestomach or unilateral stimulation of either the ventral or the dorsal forestomach wall, respectively). The following stimulation parameter was used: 0.3mA, 0.2ms, 10Hz, 20s On, 40s Off. Six additional female rats with implanted patch electrodes served as unstimulated shams. A seventh sham female rat was dropped from the study because of the presence of a large mammary tumor detected on experimental day 34. Both groups had ad lib access to a 45% high-fat diet (Research Diets; D12451; 45 kcal% fat) starting three months prior to surgical implantation of the patch electrodes and were then maintained on the same 45% high-fat diet throughout the duration of the experiment. Following completion of the study, three of the eight previously stimulated female rats (five were dropped because of failure of their back mounts) were further stimulated bilaterally for 14 days (stimulation parameter: 0.9mA, 0.2ms, 10Hz, 20s On, 40s Off). Four of the six female shams with intact back mounts served as controls. Ad lib intake of the 45% high-fat diet was continuously monitored for each individually housed female rat throughout the duration of the study using the BioDAQ automated intake monitoring system from Research Diets.
Completeness: This dataset is complete.
Subjects & Samples: Adult female (n=15) Sprague-Dawley rats (RRID:RGD_737903) were used in this study.
Primary vs. derivative data: The primary data consist of a recording of feeding behavior for individual subjects collected over the course of the experiment in a spreadsheet XLSX format. The derivative folder contains the transformed primary data located in the primary folder. The data consist of summative feeding data in a multiworkbook spreadsheet and the endpoint measurement of body fat and blood glucose levels. Thumbnail graphs of the transformed data are included. As back mount failure occurred starting six to eight weeks post-surgery, only the data from experimental weeks completed (i.e., the full seven days) prior to failure was used in the derivative excel files and companion thumbnails.
Files
1 - 0 of 0 files
About this dataset
Publishing history
Cite this dataset
Tags
References
Is Supplemented by
Phillips, R., Jaffey, D., & Powley, T. (2021). Protocol for chronic implantation of patch electrodes on the gastric muscle wall of the rat v1. https://doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.b2qgqdtw
