Effect of chronic gastric electrical stimulation on the feeding behavior of diet-induced obese male Sprague-Dawley rats consuming a 45% high-fat diet
Microstructural analysis of food intake as a behavioral endpoint to determine the effect of chronic gastric electrical stimulation on the consumption of a 45% high-fat diet by diet-induced obese male Sprague-Dawley rats
Dataset Overview
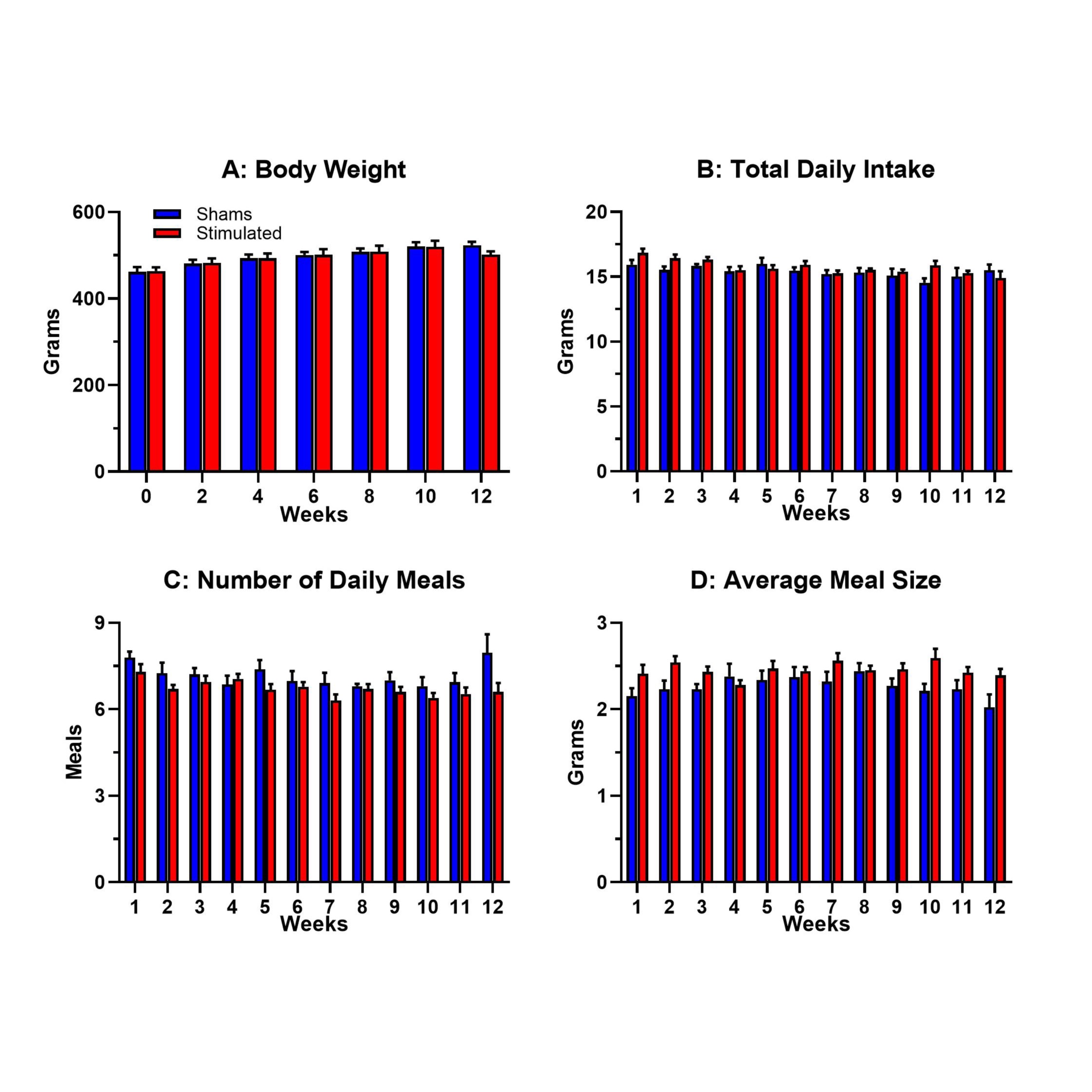
Study Purpose: We've previously reported on the feeding behavior of healthy adult male rats that were presented with a novel high-fat diet challenge paired with gastric electrical stimulation. As changes in feeding behavior were observed in that study (i.e., stimulated male rats ate fewer meals that were larger in size), we repeated the experiment in male rats that had been maintained on a 45% high-fat diet for three months prior to the onset of gastric electrical stimulation to determine if diet-induced obese male rats similarly adjust their feeding behavior in response to chronic stimulation.
Data Collection: Microstructural analysis of food intake as a behavioral endpoint to determine the effect of chronic gastric electrical stimulation on the consumption of a 45% high fat diet by diet-induced obese male Sprague-Dawley rats.
Primary Conclusion: Stimulated and unstimulated male rats did not differ in body weight and food intake throughout the twelve-week study. Both groups did not differ at the end of the study in body fat content and blood glucose levels.
Curator's Notes
Experimental Design: Following three months of ad libitum access to a 45% high-fat diet (Research Diets; D12451; 45 kcal% fat), 14 male Sprague-Dawley rats were implanted with patch electrodes at a location on the forestomach muscle wall known to contain a high density of vagal mechanoreceptors. Eight rats were then continuously stimulated for 12 weeks using a pulse parameter known to increase the number of gastric contractions (0.6mA, 0.2ms, 5Hz, 20s On:40s Off) while the remaining six rats served as unstimulated shams. Ad lib intake of the 45% high-fat diet was continuously monitored for each individually housed rat throughout the study using the BioDAQ automated intake monitoring system from Research Diets.
Completeness: This dataset is complete.
Subjects & Samples: Adult male (n=14) Sprague-Dawley (RRID:RGD_737903) were used in this study.
Primary vs derivative data: Within pool-1 is the primary data for individual subjects in spreadsheet XLSX format. The derivative folder contains the transformed primary data located in the primary folder/pool-1 folder.
Files
1 - 0 of 0 files
About this dataset
Publishing history
Cite this dataset
Tags
References
Is Supplemented by
Phillips, R., Jaffey, D., & Powley, T. (2021). Protocol for chronic implantation of patch electrodes on the gastric muscle wall of the rat v1. https://doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.b2qgqdtw
