Electrochemical measurement of kanamycin in whole blood for implant longevity evaluation
Real-time electrochemical measurements using aptamer sensor for kanamycin in human whole blood.
Dataset Overview
Study Purpose: This work evaluates the life-time of the structural-switching aptamer sensors in the whole blood using in vitro blood circulation setup as the first step toward implantable usage.
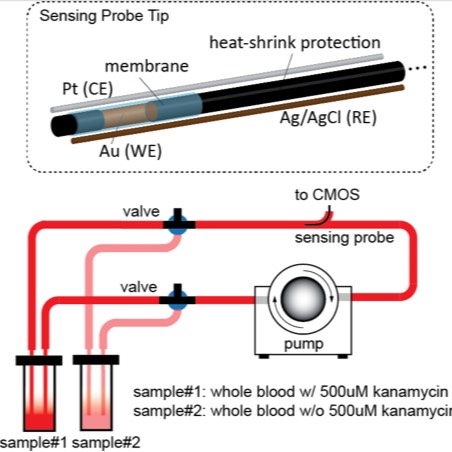
Data Collected: The device consists of a 3-electrode sensing probe with the tip of the working electrode (WE) functionalized with the antibiotics aptamers. Square-wave voltammetry (SWV) is used to continuously track both the signal peak and the background current at 5 sec temporal resolution. The sensing probe features a diameter of 800um and is inserted through a 18G catheter. Two samples of whole blood (EDTA treated), spiked with either 500uM kanamycin or SSC 1x (saline sodium citrate) buffer, are alternated toward the sensor to evaluate the degradation of the aptamer sensitivity and the degree of drift.
Primary Conclusion: None stated
Curator's Notes
Experimental design: One human blood vessel and 9 ml of human blood is used to test aptamer sensors.
Completeness: This dataset is complete.
Subjects & Samples: 9 mL of human blood, unspecified age and sex.
Primary vs derivative data: Primary data contains Square-wave voltammetry (SWV) files .pss and the file format used by PalmSense Inc. It is a file containing Linear Sweep Voltammetry method with the parameters of the sweep. Derivative folder contains Matlab processed data and sweep current ridings.
Code Availability: Please note that most of the code is made available as .v files. These .v files are Verilog hardware description language (HDL). The primary product is the chip design specifications in the code folder, which contain the following:
- Chip design hardware-language scripts for digital controller synthesis: FSM_TOP.v: verilog script for microcontroller design
- Chip design hardware-language scripts for digital controller synthesis: FSM_TOP_wi_tb.v: testbench for microcontroller block
- Chip design hardware-language scripts for digital controller synthesis: scan_chain_TOP.v: verilog script for data downlink design
- Chip design hardware-language scripts for digital controller synthesis: scan_chain_TOP_wi_tb.v: testbench for data downlink block
Important Notes: The protocol, both in the documents and protocol folder, is highly informative.
Files
0 - 0 of 0 files
About this dataset
Publishing history
Cite this dataset
Tags
References
Is Supplemented by
Chien, J.-C., E. Rangel, A., & T. Soh, H. (2019). Wireless electrochemical measurement of kanamycin in whole blood v1. https://doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.j8nlk5dydl5r/v1
