Endorgan-specific Pseudorabies (PRV) infection in mouse kidney and liver
This dataset establishes dissection and clearing techniques for kidney- and liver-innervating ganglia
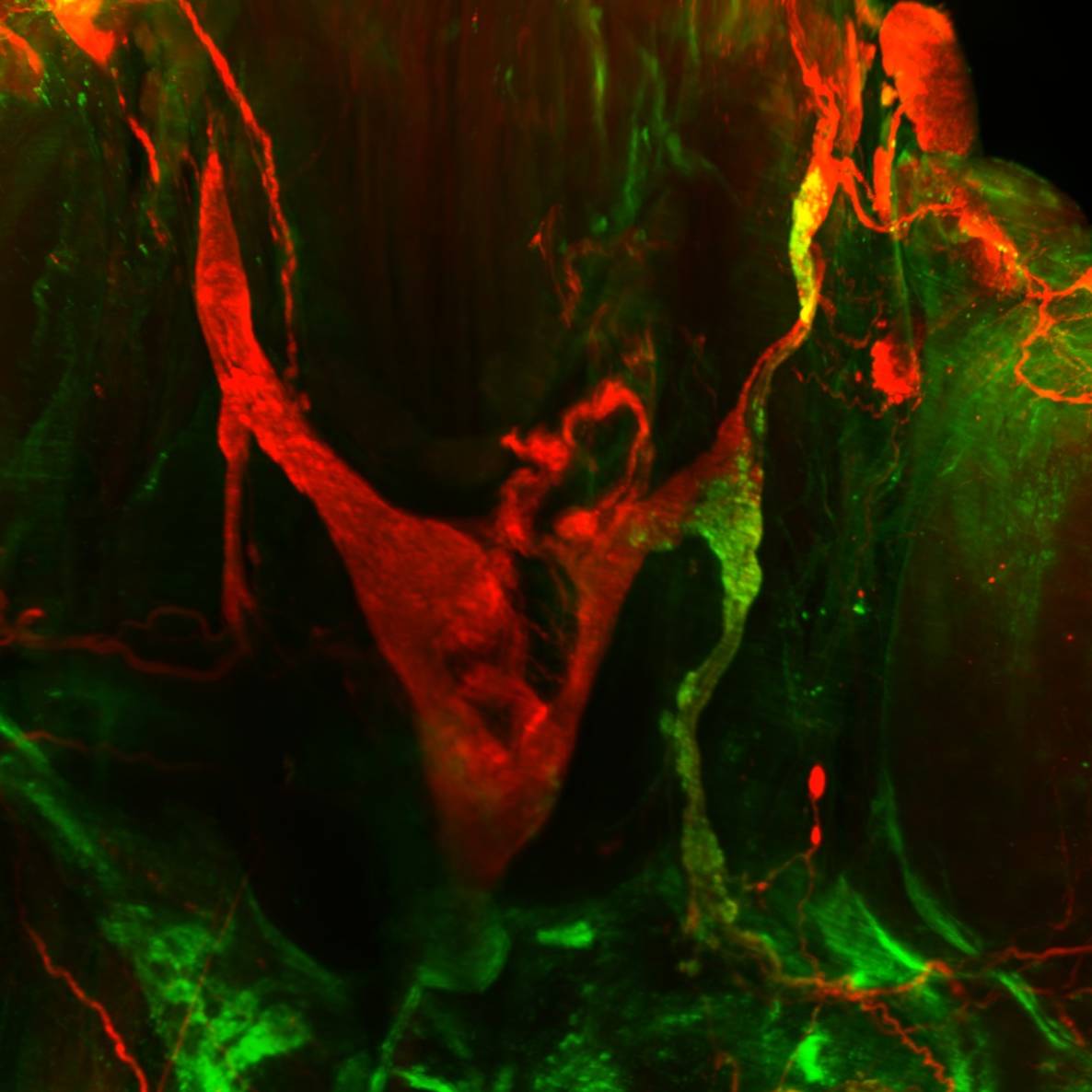
Dataset Overview
Study Purpose: To establish dissection/clearing method for kidney- and liver-innervating ganglia using endorgan-specific Pseudorabies (PRV) infection.
Data Collection: Light-sheet microscopy and confocal microscopy were used to collect high-resolution image files.
Primary Conclusion:
Kidney: We generated n=6 samples with PRV injection in the kidney. iDISCO tissue clearing and staining for tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) revealed excellent detail about the celiac complex that consists of the major celiac ganglia (a triangle-shaped structure), supra-renal ganglia, aortico-renal ganglia, and splanchnic nerves. The co-localization with PRV labeling identified the majority of kidney innervating post-ganglionic neurons are found in the aortico-renal ganglia and to a lesser extent in the supra-renal ganglia. The main celiac ganglia were largely void of PRV labeling.
Liver: We generated n=3 samples with PRV injection in the liver. iDISCO tissue clearing and staining for PRV and TH revealed that most liver innervating post-ganglionic neurons are found in the main celiac ganglia of the celiac complex. Many post-ganglionic neurons were also found in the aortico-renal ganglia and to a lesser extent in the supra-renal ganglia.
Thus, the celiac ganglia are distinctly providing sympathetic innervation to the liver, but not to the kidney, while the aortico-renal and supra-renal ganglia provide innervation to both kidney and liver.
Curator's Notes
Experimental Design: Mice (ranging from 7 to 23 weeks old) were anesthetized with isoflurane/oxygen. An incision was made by pulling straight up on the skin at the left side of the spine below the ribs to expose the left kidney and make a sagittal cut to expose the muscle. Then muscle layers were cut to make the kidney or the liver lobes accessible. Individual injections were distributed across the organ with green fluorescent protein-expressing PRV. Infected mice were euthanized, the left kidney or liver was dissected and subjected to iDISCO tissue clearing and staining for PRV and TH.
Completeness: This dataset is a part of a larger study: Genetically-based neuro-modulation of adipose tissue functions.
Subjects & Samples: Female (n=1), male (n=7), unknown sex (n=1) adult mice of mixed genetic background were used in this study.
Primary vs. derivative data: Primary and derivative folders are organized by subject identification, then by sample stained. The primary folder contains raw (.ims and .tif) microscopic images. The derivative folder contains image data (JPEG2000 and OME-TIFF) derived from primary images (.ims).
Important notes: This dataset is currently undergoing image registration and will be updated once this process is complete.
There is an associated article published: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00079.2021
Files
1 - 0 of 0 files
About this dataset
Publishing history
Cite this dataset
Tags
References
Described by
Torres, H., Huesing, C., Burk, D. H., Molinas, A. J. R., Neuhuber, W. L., Berthoud, H.-R., Münzberg, H., Derbenev, A. V., & Zsombok, A. (2021). Sympathetic innervation of the mouse kidney and liver arising from prevertebral ganglia. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 321(3), R328–R337. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00079.2021
Is Supplemented by
Huesing, C., Muenzberg, H., Zsombok, A., & Derbenev, A. (2021). Peripheral PRV injection - Kidney & Liver Protocol v1. https://doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.bujanuie
