In vitro imaging of mechanosensitive submucous neurons in the porcine colon
This dataset is about electrophysiological experiment on porcine colonic submucosal enteric neurons. The neurons were challenged with 2 different mechanical stimuli (compression and stretch). Neuronal responses to the stimuli were recorded and analyzed.
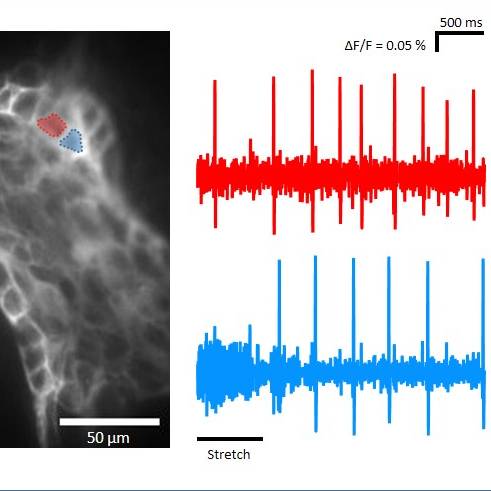
Dataset Overview
Study Purpose: In this study, we investigated the sensitivity of enteric neurons to mechanical stimuli comparing tissue samples from porcine proximal and distal colon.
Data Collection: An ultrafast neuroimaging technique was combined with a voltage sensitive dye to detect action potential discharge from enteric neurons. Changes in fluorescence intensity were recorded by an ultra-fast complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) camera system (256 × 256 pixels DaVinci-1K; RedShirt Imaging LLC) with a frame rate of 1.25 kHz. The combination of CMOS camera and a 40 × oil immersion objective lens resulted in a spatial resolution of 2.2 µm2 per pixel. Fluorescent signals were recorded and further analyzed by using the Turbo SM 64 software (RedShirt Imaging LLC; http://www.redshirtimaging.com). Neuronal viability was verified by applying 100 µM nicotinergic acetylcholine receptor agonist nicotine directly onto single ganglia by local pressure application (PDES-2lL; npi electronic GmbH, Tamm, Germany). Raw data of neuroimaging experiments were analyzed using the Turbo SM 64 2.1.0.0 or Neuroplex 10.1.2 software (RedShirt Imaging LLC; http://www.redshirtimaging.com). The proportion of mechano-sensitive neurons, MEN, and their burst frequency, defined as the number of action potentials divided by the overall duration of spike discharge, was calculated.
Primary Conclusion: None stated
Curator's Notes
Experimental Design: Tissue samples were taken from apparently healthy pigs (Leine-Fleisch GmbH, Laatzen, Germany), placed in ice-cold oxygenated Krebs solution for preparation, and immediately dissected in ice-cold oxygenated Krebs solution for preparation to obtain whole-mount inner submucosal plexus preparations. Samples were used for ultrafast neuroimaging technique combined with a voltage sensitive dye (VSD) as well as for immunohistochemistry. In order to stain selected submucosal ganglia, VSD Di-8-ANEPPS (20 μM) was applied directly into the ganglion at moderate pressure (≤ 0.5 bar). The viability of ganglia was proven by applying 100 μM nicotine on the surface of a ganglion. Mechanical stimulation included compression and tension of submucosal neurons. Compression was induced by intraganglionic volume injection of experimental Krebs solution at 0.5 bar for 500 ms. Tension of the entire ganglia was performed bidirectionally by moving a self-constructed stretching tool in opposite directions perpendicular to the ganglion axis. The preparations were examined with an inverted microscope equipped with an appropriate filter set. Pictures were acquired with a Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) camera connected to a computer and controlled by Turbo SM 64 Software. Primary antibodies against Hu, Chat, SP, and NOS were used. Specimens were first incubated in Triton X-100 (0.5%)/PBS/NaN3 (0.1%)/horse serum (4%) for 1 h at room temperature followed by 12h incubation with the primary antibodies, respectively. After incubation for 2 h at room temperature with the respective secondary antibodies, specimens were washed in PBS and coverslipped with a solution of PBS/NaN3 containing 65% glycerol. The preparations were examined with an epifluorescence microscope equipped with appropriate filter blocks. Pictures were acquired with a camera connected to a computer and controlled by Olympus cellSens Standard Software.
Completeness: This dataset is part of the larger study: In Vitro Imaging of Mechanosensitive Submucosal Neurons.
Subjects & Samples: Male (n=31) and female (n=23) adult domestic pigs age between 7 and 24 weeks were used in the study.
Primary vs derivative data: Voltage sensitive dye imaging data was automatically processed and recorded as a change in fluorescence intensity for neurons as Excel tables for two experimental groups: subjected to either compression or stretch stimulus. Primary data in each of the experimental groups are organized by the subject and then sample name, respectively. The approximate size of the data set is around 1 GB.
Important Notes: This dataset is currently undergoing image registration and will be updated once this process is complete.
Files
1 - 0 of 0 files
About this dataset
Publishing history
Cite this dataset
Tags
References
Is Supplemented by
Mazzuoli-Weber, G., Elfers, K., & Katharina Filzmayer, A. (2021). Mechanosensitive enteric neurons: incidence and abundance in the porcine submucosal plexus with ultrafast neuroimaging and immunhistochemical techniques v1. https://doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.btv3nn8n
Mazzuoli-Weber, G., Elfers, K., & Katharina Filzmayer, A. (2020). Mechanosensitive enteric neurons: incidence and abundance in the porcine submucosal plexus with ultrafast neuroimaging and immunhistochemical techniques v1. https://doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.bpcamise
Described by
Filzmayer, A. K., Elfers, K., Michel, K., Buhner, S., Zeller, F., Demir, I. E., Theisen, J., Schemann, M., & Mazzuoli-Weber, G. (2020). Compression and stretch sensitive submucosal neurons of the porcine and human colon. Scientific Reports, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70216-6
